Computer-aided surgery is used in a daily clinical workflow for safer surgical interventions. Navigation systems work based on a tracking model, which helps in the correlation of a patient’s coordinates to the preoperative or intraoperative digital medical imagery. There are two main types of navigation systems available in the market today. They are the infrared (optical) systems and electromagnetic systems. Both systems perform the same functions. However, the technology used to provide the information to the surgeon is very different.
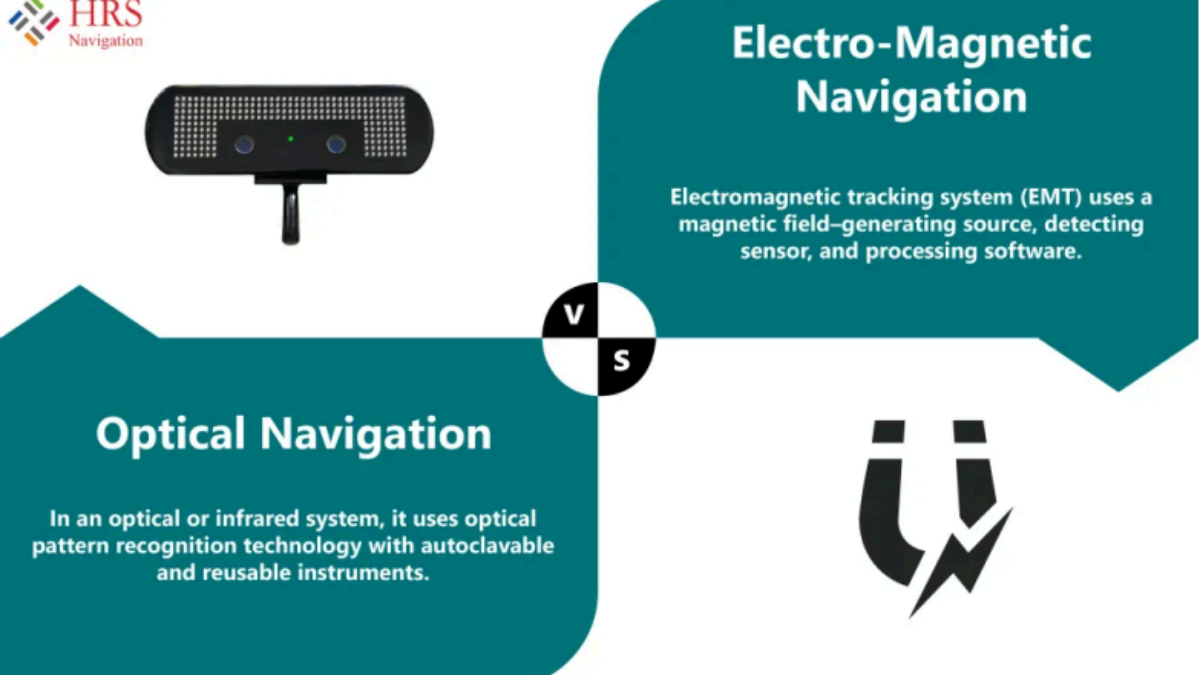
An electromagnetic tracking system (EMT) uses a magnetic field–generating source, detecting sensor, and processing software. The registration between the coordinate system of the pre-interventional patient scan and that of the tracking system happens in an electromagnetic field of known geometry. This is performed by planning about 5 to 9 landmarks in the image coordinates and the electromagnetic tracking coordinates by measuring their corresponding points with the sensor.
An optical system or infrared system uses patient trackers and probes for registration procedures on prominent landmarks. The line of sight within the camera range and localizers must be maintained throughout for real-time navigation. T o detect the probe, the patient tracker and probe should be visible to the camera simultaneously.
Why do Surgeons prefer Optical Navigation over EM Navigation systems?
- Several factors possibly affect the precision of the navigation system, such as the difference in tracking devices, registration method of anatomical landmarks, and motion centers.
- EMT systems are less recommended due to the following inconveniences faced by medicos.
- These systems are influenced by the EM interferences due to the presence of medical diagnostic devices or ferromagnetic objects nearby the field generator, distorting the transmitting signal and resulting in deviated accuracies.
- Registration is a time-consuming process and does not consider the deformations of the airways caused by the respiratory motion of the patient.
- Wired instruments causing inconvenience in handling.
- Interference with cardiac pacemakers and cochlear implants. Cables are attached to electromagnetic tracking sensors.
- Instruments free of ferromagnetic properties must be used (eg:- titanium) to maintain accuracy. Affected by metal artifacts, metal retractors or drilling devices or ultrasonographic probes can cause electromagnetic navigation errors.
Advancements have reached a point where the preoperative setup, registration time, precision, and accuracy associated aren’t part of the hassles faced by surgeons or medicos anymore. easyNav™is a consumables navigation system that works purely based on optical (infrared) tracking of autoclaved trackers assuring excellent accuracy.
The accuracy and reproducibility of this optical navigation system are higher than those of electromagnetic navigation systems. This is mainly because the registration and real-time navigation are only dependent on the tracker and probe visibility to the infrared camera. No continuous exposure to EM radiation and artifacts caused in the process. The patient registration on the prominent landmarks of the patient’s anatomy makes it entirely consumables and assures that superior accuracy is maintained throughout the surgical procedure.